$03 Emission Related Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC)
A diagnostic trouble code (DTC) indicates that the enable criteria for a monitor test failed outside of a minimum or maximum test limit. If the MIL is illuminated, tailpipe emissions have exceeded 1.5 times the Federal Test Procedure (FTP) standards. MODE $03 reports a DTC once the MIL is commanded ON. This can occur on the first or second consecutive trip. A DTC with the MIL ON is called a confirmed or current DTC. If the MIL is OFF and a DTC is still present, this is referred to as a history DTC. A history DTC remains in memory for 40 warmup cycles if the same code does not reoccur. It can also be cleared using a scan tool or by removing power from the ECM for a while. The length of time depends on the manufacturer.
Defining a Diagnostic Trouble
A five-digit alphanumeric code represents all DTCs. The first letter indicates the function of the monitored component or system that has failed:
P = Powertrain
B = Body
C = Chassis
U = Indicates a network or data link code
The second digit is represented by a number that indicates who is responsible for the code:
0 = Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE)
1 = Manufacturer specific
The third digit indicates the specific system in question. Numbers one through seven indicate a powertrain-related problem. The number eight is reserved for non-powertrain-related problems:
0 = Total system
1 = Air/Fuel metering control
2 = Air/Fuel metering control for injector circuit malfunctions only.
3 = Ignition system or misfire
4 = Emissions Control
5 = Vehicle Speed Control/Idle Control system
6 = ECM and Computer Input/Output Circuits
7 = Transmission
8 = non-Powertrain related
The fourth and fifth digits represent the component, system, or area experiencing the problem. DTC P0306 is described as:
P = Powertrain related
0 = Manufacturer-defined DTC
3 = Ignition system or misfire related problem
06 = Cylinder #6 misfire detected. This MODE retrieves all stored emission-related DTCs from the PCM.
Types of Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC)
The ECM can set two kinds of DTC.
1. Functionality DTCs are related to electrical problems set by an open and short circuit. The image below demonstrates a functionality DTC.

2. Rationality/Normality/Plausibility DTCs are performance-related problems. They are set by comparing similar inputs/outputs to see if they make sense. The customer's concern is loss of power under load. The image below shows three related PIDS: TPS, MAP, and RPM. In this case, the ECM must determine which of the three does not make sense. Can you identify the outlier PID that the ECM might flag as incorrect?

Live by codes, die by codes. Sometimes, the ECM can be fooled because the reporting component is malfunctioning. The BARO and FTP PIDs must be checked KOEO and KOER to start an EVAP diagnosis. A DTC for an out-of-range sensor will not be set if the BARO or FTP reports in the yellow zone. This can lead to a false DTC, like a Large Leak because the FTP is not reporting the correct EVAP system pressure. If the BARO reports in this range, it could cause a driveability concern or the suspension of non-continuous readiness monitor tests.

Setting a Pending (2 Trip) or confirmed (1 or 2 Trips) Diagnostic Trouble Code
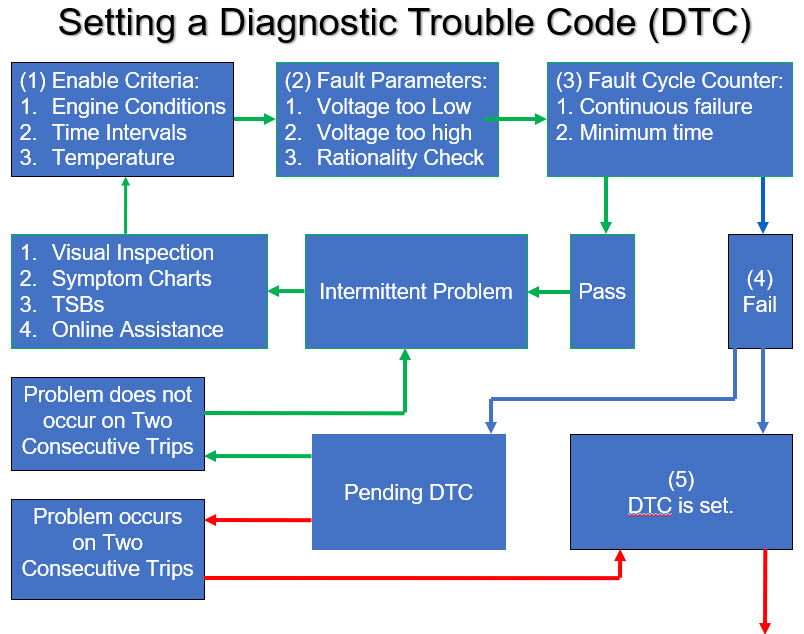
Setting a pending (2 Trips) or confirmed (1 or 2 Trips) Diagnostic Trouble Code requires numerous steps. Think of it as a sequence of events. If the steps in the sequence occur, a pending or confirmed DTC will be set into memory. A DTC is not easily set because the ECM/PCM needs to be sure the problem actually exists. The first step in the sequence requires specific enable criteria to be met. This will vary for each DTC and between different manufacturers.
(1) Enable Criteria: For the ECM/PCM to monitor a system, specific operating conditions must be met. If the enable criteria are not met, nothing will happen, and a DTC cannot be set for the circuit being monitored. If the enable criteria are met, then ECM/PCM moves on to the next step.
(2) Fault Code Parameters: As long as the enable criteria are met, the ECM/PCM will check the circuit value against internal software. The circuit is checked for voltages that are too low or too high. Additionally, the input is checked against other related inputs to see if the value makes sense. Review the Rationality/Normality/Plausibility section above.
(3) Fault Cycle Counter: The ECM/PCM monitors the circuit to see if the problem is continuous for a minimum amount of time. If it does not last a minimum amount of time, the system passes, the problem is intermittent, and the technician must refer to other resources, from a visual inspection to online assistance. If the problem is continuous and exceeds the minimum time, the circuit fails, and either a pending is set, and it will have to fail on two consecutive trips; or a confirmed DTC is set.
(4) If the issue lasts long enough, either a two-trip Pending DTC or a confirmed DTC and Freeze Frame are set.
If the issue does not last long enough, it is back to basics and the process starts all over again.
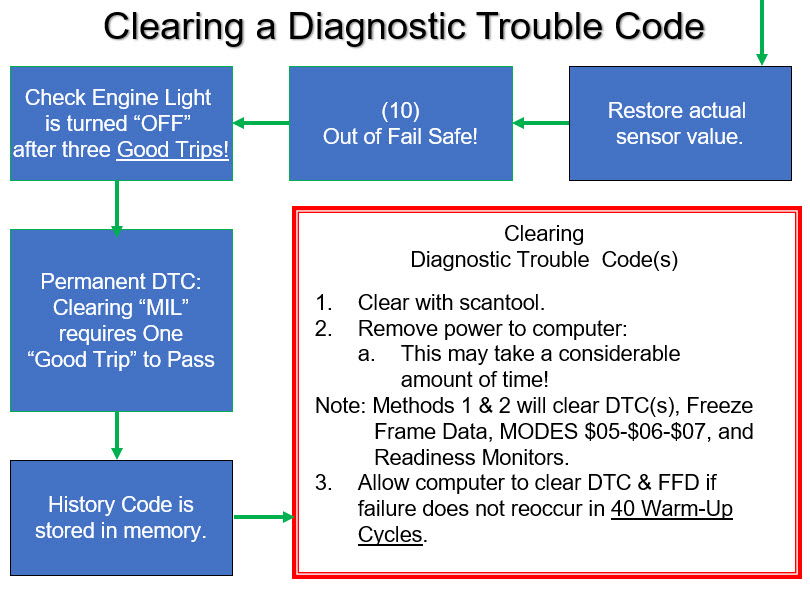
(6) At this point, the MIL is Commanded On.
(7) The ECM/PCM will use a default value to keep the vehicle running and the customer's vehicle off the tow truck. Note: The global side of the scan tool cannot display a default value, it must display the actual sensor value at the time of the failure. The regulations allow the ECM/PCM to display a default value on the enhanced side of the scan tool. A default value will only be used if a confirmed DTC is set, and the MIL is Commanded ON.
(8) At this point, the ECM/PCM continues to monitor the circuit while the enable criteria are being met.
(9) If the system passes, the ECM/PCM restores the actual value and continues.
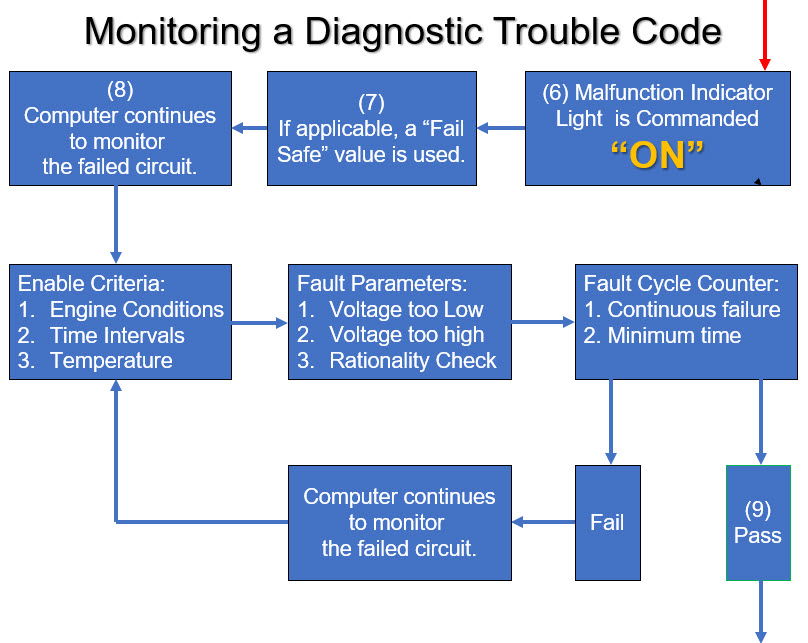
(10) Once the value is restored, the system is out of fail-safe and returned to normal. For OBDII vehicles, the MIL will remain on for three good trips. Once three good trips are achieved, the MIL is Commanded Off. The DTC remains in memory and is called a History DTC. Permanent DTCs (PDTC) were introduced in 2010 and phased in through 2012. They are standard on all 2012 and newer vehicles. If a scan tool is used to clear the DTC, the Freeze Frame will be cleared. For a PDTC, it will remain in the memory and can be cleared after one Good Trip. For more information, click on this link PDTC.