Unified Diagnostic Services
This section will address "E/E Diagnostic Test Modes: Onboard Diagnostics II on Unified Diagnostic Services (OBDonUDS), SAE 1979-2/3. It is a Worldwide Harmonized OBD Vehicle System. This system incorporates SAE J1979-2/3 and ISO 14229 standards.
The most critical information needed to understand SAE 1979-2/3 is a solid understanding of SAE 1979/Global OBDII. Being familiar with the changes introduced by the Controller Area Network (CAN) in 2008 will make the transition easier. These changes included improvements to PIDS (MODE $01), Test Results (MODE $06), Vehicle Information (MODE $09), and Permanent DTCs (MODE $0a). This information can be viewed by clicking on this link.
- What is UDS?
- Implementation
- OBDonUDS Data Enhancements
- SAE J1979 versus SAE J1979-2 Standards
- How will this impact current I/M programs?
1. Unified Diagnostic Services (UDS) is a new software program that will reformat how diagnostic information is displayed using a Generic Scan Tool (GST). It will organize diagnostic services into user-friendly groups and provide more detailed diagnostic information. These new UDS services for OBD will be called “OBDonUDS" and will use SAE J1979-2/3 standards.
It will still use the CAN communications protocol, but the message will have seven layers instead of the current five. It will still use CAN communication (i.e., pins 6 + 14) through the current OBD-II connector (SAE J1962). These vehicles must use SAE J1979-2 for all OBD-II communications and will not respond to currently used protocols. OBDonUDS includes classic J1979 Modes $01 to $0A and features such as DTC-specific Readiness Flag test results and IUMPR to OBD, but they will be referred to Services, not Modes.
SAE 1979-2, OBDonUDS, will include light-duty, medium-duty, and heavy-duty Spark and Compression engines. SAE 1979-3, ZEVonUDS, will cover Zero-Emission Vehicles.
2. Implementation of OBDonUDS is for all LD, MD, HD, and ZEV vehicles. The system will be installed on some 2025/2026 model-year vehicles. The number of vehicles equipped with the services each model year is up to the manufacturers. It is expected that full implementation will occur with the 2027 model-year vehicles.
3. OBDonUDS Data Enhancements will include 1) expanded readiness group categories, 2) redefined readiness completion requirements for misfire, fuel system, and comprehensive components, 3) added DTC status byte to provide DTC-specific readiness and other DTC-specific info (i.e., pending status, confirmed status, and complete this drive cycle), 4) Enhanced freeze frame support to 5 DTCs where each DTC will have two allotted freeze frames (one for the first occurrence and the second for the most recent event), 5) expanded DTC naming to 3 bytes (no longer using 2-byte DTCs), added failure type byte (FTB) to current DTC names to create more DTCs available for use, 6) and added evaporative system (EVAP) sealing functionality.
4. SAE J1979 versus SAE J1979-2/3 Standards Services:
| OBD Functionality | SAE J1979 (OBDII) | SAE 1979-2 (OBDonUDS) |
| Powertrain Data/Readiness Status | MODE $01 | Service $22 |
| Freeze Frame Data | MODE $02 | Service $19/$04 |
| Confirmed DTC | MODE $03 | Service $19/$04 |
| Clear Emissions Data | MODE $04 | Service $14 |
| DTC Test Results | MODE $06 | Service $19/$06 |
| Pending DTCs | MODE $07 | Service $19/$42 |
| Request Control | MODE $08 | Service $31 |
| Vehicle Information (CAL ID and CVN) | MODE $09 | Service $22 |
| DTC In-Use Monitor Performance Ratio (IUMPR) | MODE $09 | Service $19/$06 |
| Permanent DTCs | MODE $0a | Service $19/$55 |
*List of DTCs within each Readiness Group | No Support | Service $19/$56 |
| *List of DTCs that support IUMPR* | No Support | Service $19/$1A/$91 |
| *List of DTCs that support DTC Test Results* | No Support | Service $19/$1A/$92 |
| *Supplemental Monitor Activity Data* | No Support | Service $19/$06 |
*New to OBDonUDS* |
To better understand MODE $09 and IUMPR, refer to the section about OBDII MODES $01 - $0a.
5. How will this impact current I/M programs?
It will require a software update and possibly a scan tool hardware update to the Generic Scan Tool (GST), as well as additional memory to accommodate the new, more significant message responses. The I/M database storage must be updated to accommodate new data (both in size and format). New readiness categories will be used as additional failure criteria (more data will be needed to determine if the vehicle ran its emissions monitor test before an I/M test). The extra data can be used for fraud detection and provide more insight into the performance of emissions monitoring tests.
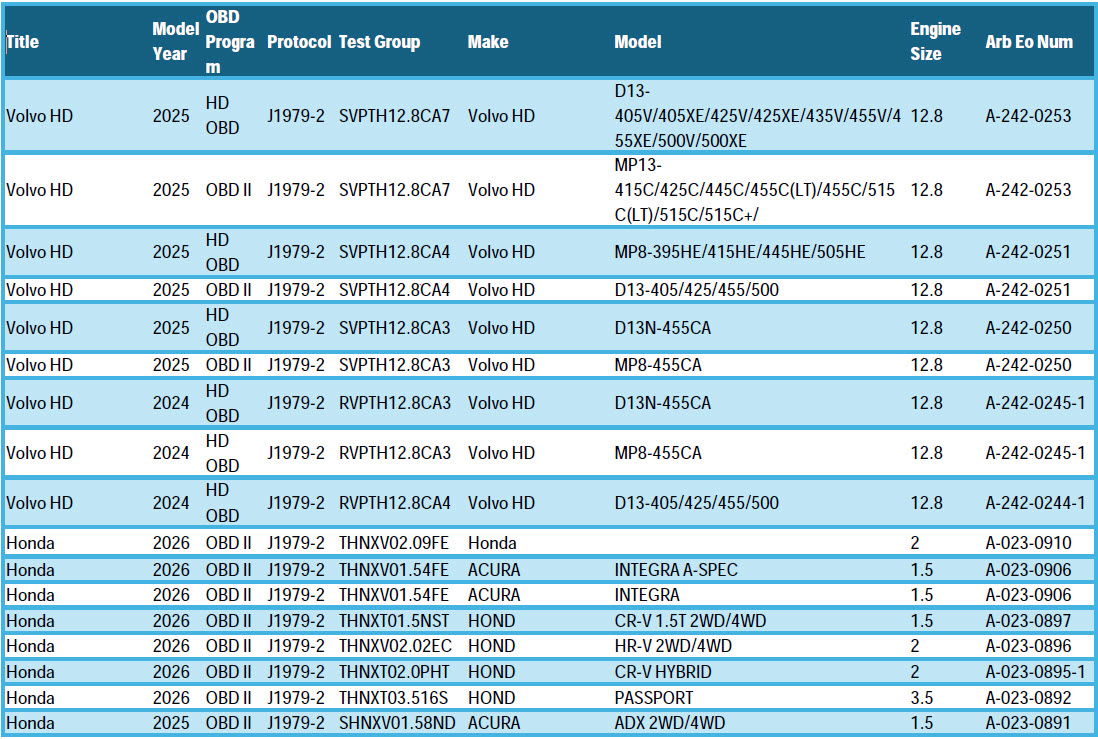
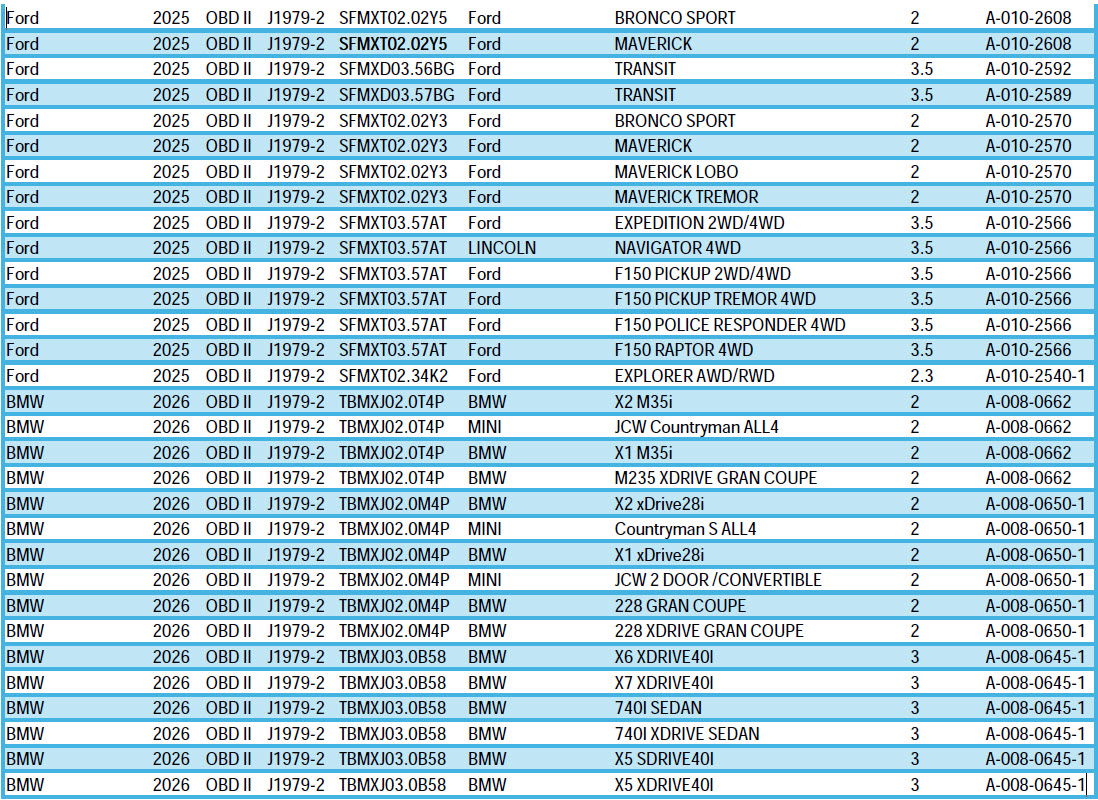
What Vehicles are Currently Certified and Equipped with Unified Diagnostic Services? (November 12, 2025)